Yes, the injury was recordable. OSHA says that lunch breaks are considered to be within assigned working hours, so the exception cannot apply. OSHA LOI July 29, 2019
Test yourself: Is this injury recordable?
Date Posted: 04/21/2025
Many injury and illness recordkeeping questions involve the “work-related” issue because every case is presumed to be work-related unless a specific exception applies, and those exceptions are narrow. To test your knowledge of this exception, consider the following scenarios from OSHA Letters of Interpretation (LOIs). Click "View Answer" below each scenario to see the answers.
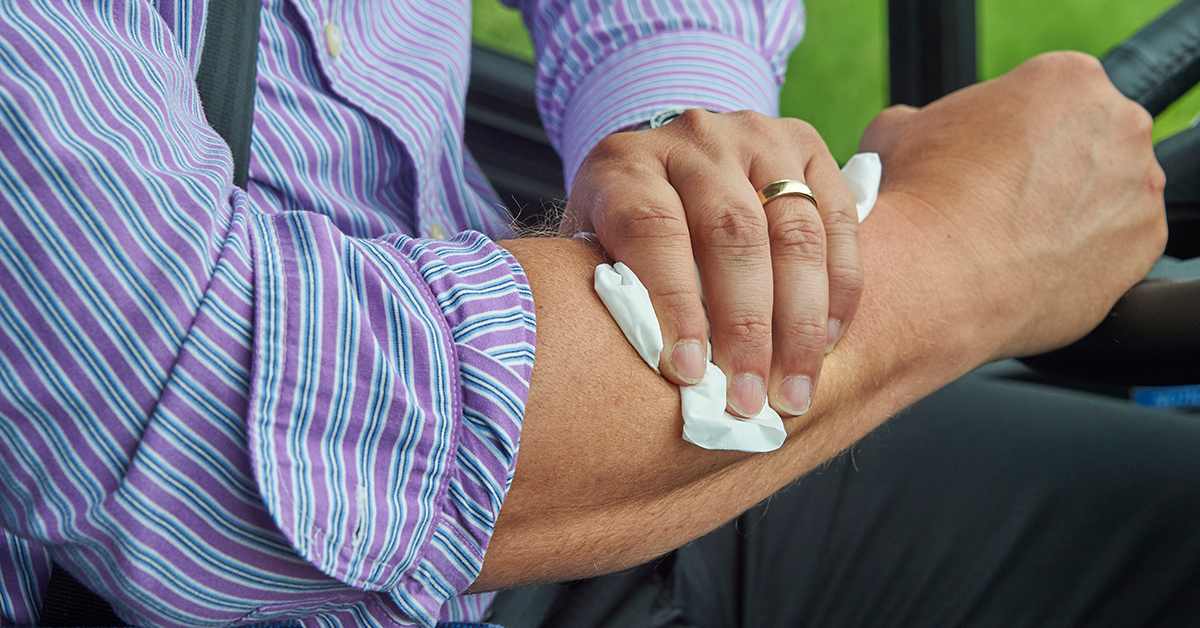
Scenario One: Employee Injury from Personal Pocketknife Use During Lunch Break
An employee cut his hand while sharpening a personal pocketknife. He was sitting in a company-owned truck while parked in the employer’s parking lot but was on his lunch break at the time. The cut required stitches.
The employer asked about the exception for cases where the injury is solely the result of doing personal tasks (unrelated to employment) at the establishment outside of the assigned working hours. Is this recordable?
Scenario Two: Employee Injury While Intoxicated
An employee was injured when his hand was caught between two objects. A post-accident drug test found that the employee was intoxicated from alcohol. The employee was a known alcoholic.
The employer asked about the exception for cases that result solely from self-medication for a non-work-related condition. Specifically, the employer asked if this could apply because the worker was self-medicating with alcohol for his condition. Is this recordable?
Yes, the injury was recordable. OSHA concluded that drinking alcohol is not a recognized treatment for alcoholism; it is a manifestation of the disorder. Therefore, the self-medication exception could not apply. OSHA LOI March 21, 2016
Scenario Three: Allergic Reaction at Company Lunch
An employee had an allergic reaction (food allergy) at a company-provided lunch and was taken to a hospital for treatment. There was no evidence of contamination, and no other employees became ill.
The employer asked about the exception when an illness is solely the result of eating, drinking, or preparing food or drink for personal consumption (which does not apply if the employee gets food poisoning from food supplied by the employer). Is this recordable?
No, the illness was not recordable. Although the exception does not apply if an employee gets food poisoning, this case involved a food allergy, which is not food poisoning. Therefore, the case is not work-related. OSHA LOI April 22, 2010
How Safety Management Suite Can Help
Once you’ve determined that a case is recordable, it must be listed on your OSHA 300 Log. The J. J. Keller® SAFETY MANAGEMENT SUITE Incident Tracking & Form 300 Tool helps you do more than simply comply with the recordkeeping requirements and complete your First Report of Injury (FROI). Find out what incidents are and are not recordable with our easy-to-use Recordable Incident Wizard and identify and address safety issues by tracking trends in your safety program.
E-mail Newsletter
Sign up to receive the weekly EHS Insider email newsletter for safety articles, news headlines, regulatory alerts, industry events, webcasts, and more.